HDHP, PPO, HSA … the acronyms and the options can seem endless when you’re evaluating health insurance plans. Choosing the right plan is an important financial decision, and it’s wise to weigh the details carefully. In this post, we’ll dig into the tradeoffs associated with choosing a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) over a traditional preferred provider organization (PPO) plan, so you can confidently choose the option that’s right for you.
What is a PPO?
Let’s start with the basics. PPOs are the most common type of health insurance plan by enrollment. When you choose a PPO, you can typically see in-network healthcare providers (including specialists) without a referral. If you want to see a provider who isn’t in your PPO’s network, you can expect paperwork and higher costs. Generally, PPOs have higher premiums than HDHPs, but much lower deductibles. Traditional PPOs do not come with the option to open a health savings account or HSA.
What is an HDHP?
An HDHP is another popular type of insurance plan — they’re the second-most common kind of health insurance plan after PPOs. Any health insurance plan (including a PPO) is considered an HDHP if it has a high-enough deductible: $1,600 for an individual and $3,200 for a family in 2024 (with those numbers rising to $1,650 and $3,300 in 2025). HDHPs have a few key characteristics:
- As the name suggests, HDHPs have higher deductibles than other plans.
- HDHPs typically have lower premiums (or monthly insurance plan costs).
- HDHPs allow you to open an HSA (Health Savings Account).
What is an HSA?
An HSA is a tax-advantaged account you can use to save for healthcare expenses. You and your employer can contribute to your HSA, and you can choose to invest the funds in the account. Your contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, meaning you can deduct your contributions from your income for tax purposes, thereby reducing your taxable income. You can withdraw the funds tax-free for qualified medical expenses, and you can take the account with you if you change jobs. HSAs are similar to the flexible spending accounts (FSAs) that come with PPOs, but offer far more flexibility in rolling over unused funds.
There’s a notable exception to HSAs’ tax-free status: currently, there are two states that don’t conform to federal tax treatment of HSAs. In New Jersey and California, HSA contributions and any realized capital gains are considered taxable income at the state level. Taxpayers are required to report these realized gains on their tax returns, as most brokerages that handle the HSAs don’t send any tax forms.
HDHP vs. PPO: Which plan is best for you?
When you evaluate a health insurance plan, there are a few key numbers you should pay attention to:
- Annual premium: What you’ll pay each year just to have insurance. Usually, this will come out of your paycheck.
- Deductible: The amount of money you need to spend on healthcare (not including your premiums) before your insurance starts to chip in. Keep in mind that preventative care is generally covered in full even before you hit your deductible.
- Coinsurance: The percentage of healthcare costs you pay after hitting your deductible, but before you hit your out-of-pocket max.
- Out-of-pocket max: The maximum amount of money you will spend out-of-pocket on healthcare that year. This includes your deductible, but not your premiums. After you hit this maximum, your insurance covers 100% of your healthcare costs.
- Employer HSA contribution: Money your employer gives you for your HSA.
You can use these numbers and the formulas below to compare the attractiveness of various healthcare plans offered by your employer. The first formula assumes you expect to hit your deductible. The variable X represents what you expect to spend on healthcare costs this year.
Net costs = Annual premiums + Deductible + (Coinsurance)(X – Deductible) – Employer HSA contributions
If you expect that your healthcare costs will be less than your deductible, use this formula instead:
Net costs = Annual premiums + X – Employer HSA contribution
When you use these formulas, keep in mind that your plan will cap your out-of-pocket spending (that’s the “Deductible + (Coinsurance)(X – Deductible)” part of the equation) at a specific number.
We know it’s easier to put this into practice with an example, so we’ll apply this framework to two Cigna plans available to Wealthfront employees a few years ago to see how they compare.
Example plan comparison: Cigna’s PPO 250 vs. Cigna’s HSA 1400
The table below shows the details of two Cigna plans that were available to Wealthfront employees a few years ago: the PPO 250 and HSA 1400. While Wealthfront covers 100% of premiums for individual employees, note that it’s more typical for an employer to cover about 80% of individual premiums and about 70% of family premiums. The HSA contributions reflected below are what Wealthfront offers employees, but average employer HSA contributions are lower at about $750.
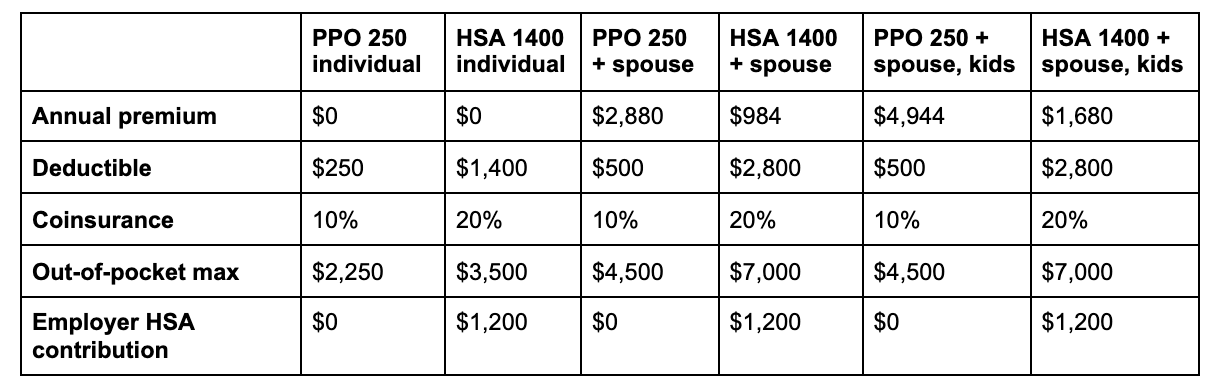
For some kinds of care (like specialist and primary care visits) you would actually pay a $15 copay per visit after hitting your deductible with the PPO rather than 10% coinsurance. For other kinds of care, like an emergency room visit, you’d pay a $100 copay with the PPO. However, these flat fees make the plans challenging to model accurately – so instead, for simplicity, we assumed you’d pay 10% coinsurance for all healthcare after meeting your deductible.
Using the formula above, here is how you’d fare at a few different levels of spending with these two plans. We’ll assume all money spent on healthcare is in-network, as out-of-network healthcare costs vary and are much higher. We’ll also assume the money you spent on healthcare is not for preventative care (which your insurance will typically pay for even before you hit your deductible).
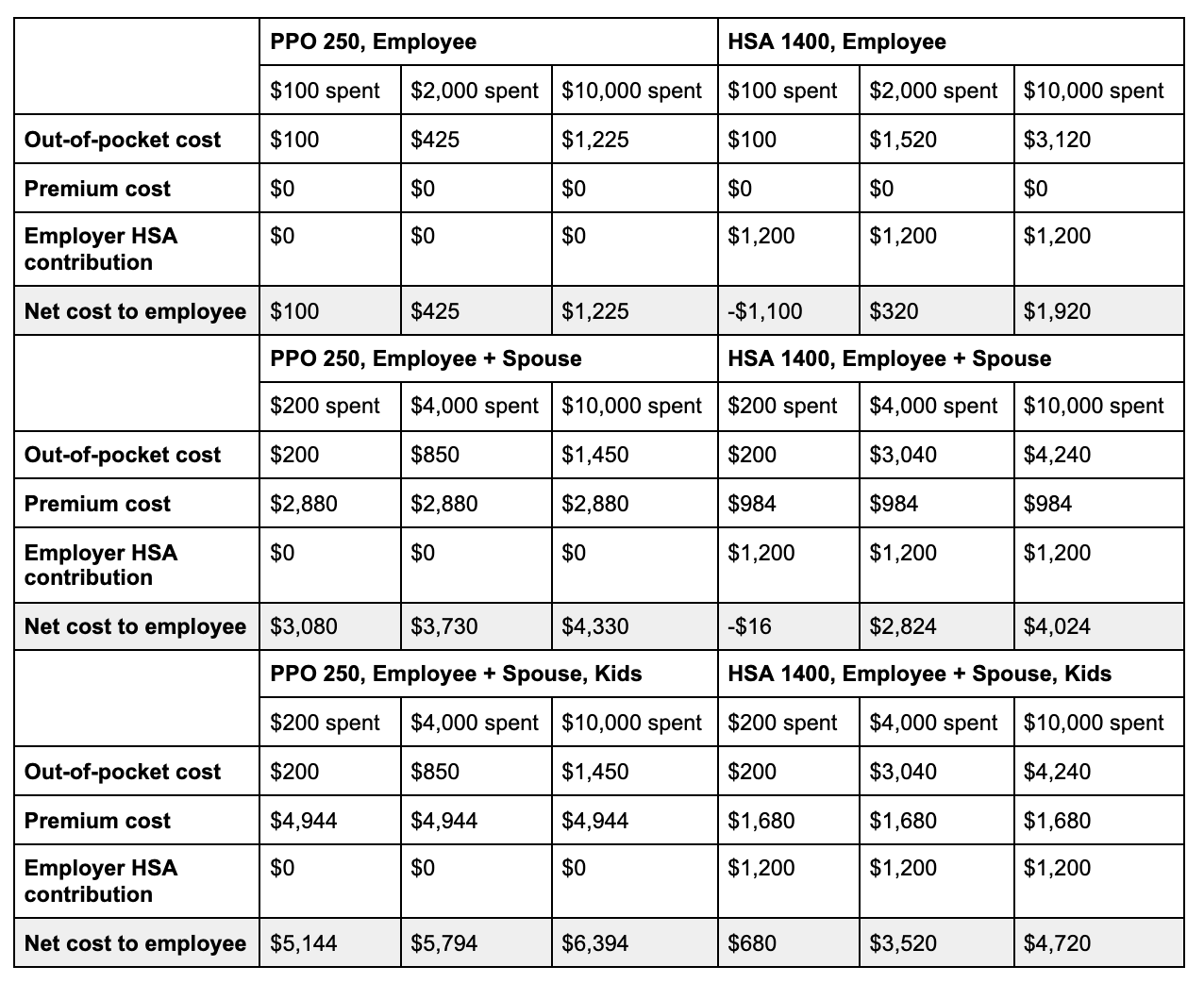
You would be indifferent between the two plans in this example if you were a single employee with $3,050 in medical expenses that year – at that level of spending, the two plans would cost you the same amount out-of-pocket. If you spent less than $3,050, you would be better off with the HDHP. If you spent more than $3,050, you would be better off with the PPO.
However, there’s no situation in which a Wealthfront employee with a spouse or family covered by these specific plans would have come out ahead with the PPO. That’s because the difference between the premiums and employer HSA contributions is larger than the difference between the plans’ respective out-of-pocket maxes. If you are comparing two plans where this is the case, you can confidently choose the HDHP.
Choosing the plan that’s right for you
The results above are specific to the two Cigna plans we examined — it’s very important that you use the formula to evaluate the actual plans you’re choosing between, as your results could be very different. We included the details of these plans to help illustrate a framework for choosing your plan, not to give broad advice about HDHPs and PPOs. The HSA 1400 offered to Wealthfront employees had what was, at the time, the lowest possible deductible for an HDHP, which is part of why it looks so much more attractive than the PPO 250 in most cases. (These numbers have changed. In 2025, the lowest possible deductible for an HDHP is $1,650 for an individual and $3,300 for a family.) HDHP deductibles can be much higher. That’s why it’s crucial that you evaluate your own plans instead of treating these as representative. If your plans have different premiums, deductibles, employer HSA contributions, coinsurance, or out-of-pocket maxes, then you could get a very different result.
How should you estimate your medical expenses?
Estimating your medical expenses for the upcoming year can be challenging, but it’s an important part of choosing your health insurance. Ask your employer if they have a calculator to help you understand what your healthcare costs might be. If there is no calculator available, here’s how to estimate costs yourself.
Start by multiplying any recurring monthly healthcare expenditures, like prescription refills, by 12 to understand the annual cost. You should also think about the long tail of medical expenses you might incur in a year. If you see your primary care doctor twice per year, you should factor in what you’d pay for those visits. You should also think about how many specialist visits you’re likely to need that year and estimate the cost of those. If you still have your medical bills from previous years, you can use them to help you ballpark the costs.
Finally, think about any larger medical costs you might face. Do you plan to start a family? Do you have a major surgery on the calendar? Are you experiencing a chronic health issue? Factor that in, too. The higher you expect your medical costs will be, the more likely you are to be better off with a PPO.
Pros and cons of HSAs
Many people are tempted to choose an HDHP solely because of the tax-advantaged nature of HSAs, but this isn’t a great reason on its own. HSAs have significant pros and cons you should be sure to factor in, along with the other details of your particular plan options.
Benefits of HSAs
HSAs have significant tax benefits now and in the future. In most states, you can invest your HSA funds and let them grow tax-free, and then you can withdraw them for qualified medical expenses without paying taxes. In other words, it’s like combining the best of a traditional IRA and a Roth IRA.
HSAs offer you an opportunity to build up even more savings for qualified medical expenses over time, because you don’t have to treat employer HSA contributions like cash and spend them the year you receive them. You can also roll any leftover money over to future years and invest it so it compounds tax-free, allowing you to offset an even larger amount of medical expenses in the future.
HSA withdrawals become more flexible after you turn 65. At that point, you can make withdrawals for purposes other than qualified medical expenses and not pay a penalty. However, it’s worth noting that you might not be eligible to make HSA contributions after you turn 65. Here’s a helpful resource on the rules.
HSA drawbacks
However, you shouldn’t overlook HSAs’ limitations just because they’re tax-advantaged. A recent report on the HSA landscape by Morningstar found that HSA fees can be high (even though Morningstar found they were decreasing overall), with custodial fees as high as 0.50%. Some HSA providers also charge fees for monthly account maintenance. These fees have the potential to eat away at your contributions and returns in a big way. Unfortunately, Wealthfront doesn’t currently have an HSA offering for clients.
The bottom line
HDHPs can be a good form of insurance for the young and healthy — especially if your employer offers you HSA contributions. But for anyone with significant medical expenses, an upcoming surgery, or a serious health condition, a PPO could be a better fit because of the lower deductible. However, if your employer offers you an HDHP with a low deductible and a generous HSA contribution, that HDHP could be a better deal than a PPO even if you expect your healthcare spending for the year will be high. We encourage you to make the decision between an HDHP and PPO based on the formula we provided, using your anticipated medical expenses, the premiums you’ll pay, your employer’s HSA contributions, coinsurance, and the deductible and out-of-pocket spending cap for the plans you’re evaluating. It might feel like a hassle, but you’ll sleep better at night knowing you selected the health insurance plan that’s right for you.
Disclosure
The information contained in this communication is provided for general informational purposes only, and should not be construed as investment, insurance, or tax advice. Nothing in this communication should be construed as a solicitation or offer, or recommendation, to buy or sell any security. Any links provided to other server sites are offered as a matter of convenience and are not intended to imply that Wealthfront Advisers or its affiliates endorses, sponsors, promotes and/or is affiliated with the owners of or participants in those sites, or endorses any information contained on those sites, unless expressly stated otherwise. Wealthfront Advisers and its affiliates do not provide legal, insurance, or tax advice. Individuals should consult an investment professional, attorney, or tax professional regarding their own specific situation.
Cash Account is offered by Wealthfront Brokerage LLC (“Wealthfront Brokerage”), a Member of FINRA/SIPC. Neither Wealthfront Brokerage nor any of its affiliates are a bank, and Cash Account is not a checking or savings account. We convey funds to partner banks who accept and maintain deposits, provide the interest rate, and provide FDIC insurance. Investment management and advisory services–which are not FDIC insured–are provided by Wealthfront Advisers LLC (“Wealthfront Advisers”), an SEC-registered investment adviser, and financial planning tools are provided by Wealthfront Software LLC (“Wealthfront Software”).
All investing involves risk, including the possible loss of money you invest, and past performance does not guarantee future performance. Please see our Full Disclosure for important details.
Wealthfront Advisers, Wealthfront Brokerage and Wealthfront Software are wholly owned subsidiaries of Wealthfront Corporation.
Copyright 2024 Wealthfront Corporation. All rights reserved.
About the author(s)
Kevin Teague is a Product Specialist at Wealthfront and a Certified Financial Planner (CFP). Prior to Wealthfront, Kevin worked at Fidelity Investments. View all posts by Kevin Teague, CFP



